Coal Prices
- Premium Low Vol (FOB Australia) $236.00/mt
- CFR China Shanxi PLV equivalent $214.26
- PLV China Netback $211.95
- PCI (FOB Australia) ~$191
- Low Vol HCC (USEC) $227
- High-Vol A (USEC) $216
- High-Vol B (USEC) $206
- CFR South China (5,500) $92.00/mt
- FOB Newcastle 20% Ash (5,500) $87.75
- CFR India West (5,500) $87.50
- CIF ARA (6,000) $119.95
- Richards Bay (5,500) $85.25
- Baltimore 3% Sulfur (6,900) $80.75
- Hampton Rds 1% Sulfur (6,000)$113.40
- Kalimantan (4,200) $51.50
Coal News
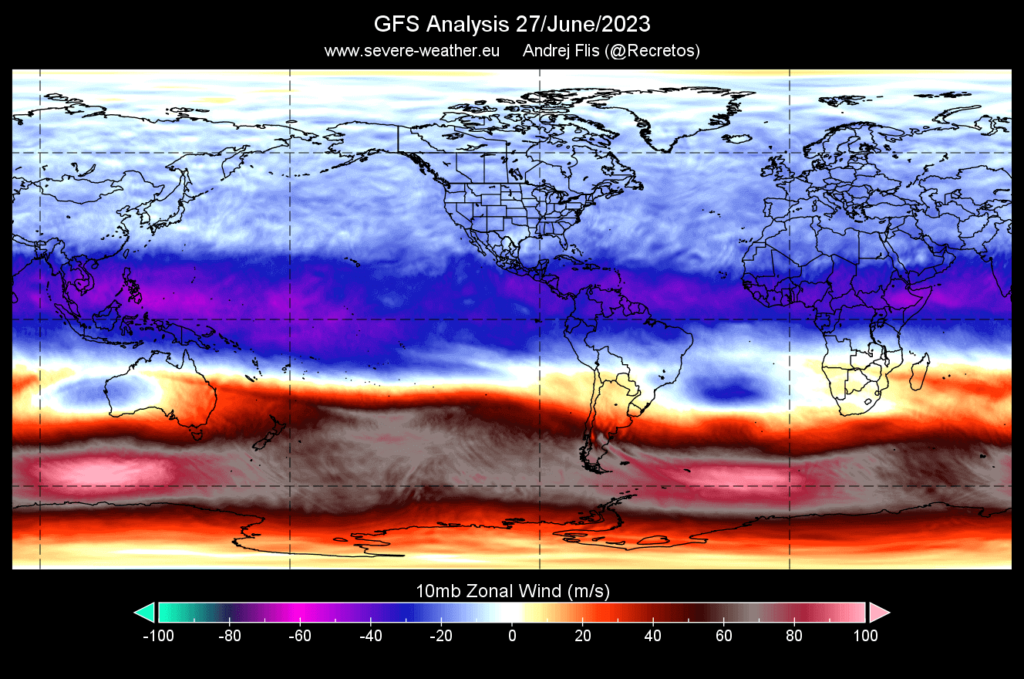
A Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO) wind anomaly is developing over the Equator, which will impact winter weather along with the El Nino event in the upcoming 2023/2024 Winter season. The QBO, known as the “heartbeat of the atmosphere,” is a regular variation of winds in the tropical stratosphere that changes direction every 14 months. The QBO phases (easterly and westerly) influence the polar jet stream and can affect winter conditions. A negative QBO phase (easterly winds) increases the chances of a weaker jet stream, sudden stratospheric warming events, and colder winters in the Northern Hemisphere, while a positive QBO phase (westerly winds) increases the chances of a stronger jet stream and milder winters. The QBO is connected to the Polar Vortex, El Nino, and other atmospheric phenomena, impacting weather patterns globally.
Coal deliveries to Pakistan have increased due to the availability of South African supply. The country had experienced a lack of supply and weak demand, but a shipment of South Africa-origin coal recently entered Pakistan. South African coal is preferred in Pakistan due to its higher calorific value and reliability. However, operational issues have reduced South Africa’s share of shipments in the past year. Planned maintenance on the rail line connecting to the Richards Bay Coal terminal in South Africa may further hinder coal exports. The price of CFR Pakistan 5,750 kcal/kg NAR coal was assessed at $100.75/mt on June 29, a 45-cent increase from the previous day.
According to data from the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), thermal coal imports by power producers in India totaled 4.66 million tons in May. This represents an 11.3% decrease compared to the same period last year and a 2.71% decrease compared to the previous month’s imports, which stood at 4.79 million tons.
LNG inventory held by major power utilities in Japan dropped to a seven-week low of 2.23 million metric tons on June 25, down 5.9% from the previous week. The inventory level is similar to that of May 7. Despite the approaching peak summer power demand season in Japan, there has been limited additional spot LNG demand due to relatively high inventories. Similarly, spot LNG demand in South Korea and China has been lackluster, with China’s buying activity slowing down after the Platts JKM price rose above $10/MMBtu. On June 28, the Platts JKM price for August was assessed at $12.049/MMBtu.
ArcelorMittal, Europe’s largest steelmaker, is preparing for a temporary shutdown of its Fos-sur-Mer site in France after an order from the French Labour Inspectorate. The shutdown is due to high emissions posing a risk to workers’ health. The company is implementing a safety plan and taking legal action against the order. The Fos-sur-Mer site has two blast furnaces and will eventually be replaced by an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) plant as part of ArcelorMittal’s decarbonization strategy. The new facilities are expected to be operational by 2027, gradually replacing three out of five blast furnaces in France by 2030.
Atlantic met coal prices remained steady on June 29, with a focus on European steel operations and limited spot market demand. US prices were stable, but confirmation of US spot demand for low-volatile coking coal was still pending. Thyssenkrupp Steel in Germany reported no impact from flooding on its operations, alleviating concerns of disruptions. ArcelorMittal announced plans to restart blast furnaces in Spain and France but also began preparations for the shutdown of BF-based operations in Fos-sur-Mer, France. Benchmark prices for US low-volatile and high-volatile coal remained unchanged. No Asia-Pacific Platts met coal assessments were published due to a public holiday. SGX reported cleared futures contracts for July, August, and September 2023.
The Chinese steel industry’s Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) increased by 14.7 percentage points to 49.9% in June, indicating a slight improvement in production and demand. The sub-index for new domestic steel orders rose by 24.1 percentage points to 51.5%, suggesting a return to expansion in steel demand. However, the increase was from a low base, and actual demand recovery remained modest. Steel production also increased due to rising demand and the completion of maintenance, with the production sub-index reaching 49.9%. However, Chinese steel demand is expected to be restrained in July due to adverse weather and a declining real estate market. The sustainability of the recovery depends on the realization of anticipated incentives, and steel production is likely to slow in line with weakening demand. China’s manufacturing activity continued to contract in June, with a PMI of 49.0%, below the 50.0% threshold for the third consecutive month.
MC Mining, a coal miner, has released an updated life-of-mine (LoM) plan and coal reserve estimate for its Makhado steelmaking hard coking coal project. The updated plan shows a 27% increase in mine life and a 25% higher yearly mine production rate. Proven and probable coal reserves have increased by 53%, and there is a significant increase in salable steelmaking hot coking coal and saleable coal. The updated plan demonstrates improved production metrics and financial returns, including higher free cash flows and post-tax net present value. The project is progressing on schedule, and the increased coal reserves are expected to enhance profitability.
Asian seaborne hot-rolled coil (HRC) prices remained unchanged with limited transactions as Chinese suppliers returned from a holiday and buyers assessed price movements. Chinese offers for HRC were unchanged, and market sentiment turned somewhat bearish due to declining futures prices. Vietnamese HRC demand is sluggish, and imports are unlikely to increase significantly. Other countries, such as India and the Middle East, saw stable or slightly higher HRC prices. South Korean and Taiwanese suppliers are negotiating prices with Japanese buyers, considering global price declines and the impact of a weaker yen.
California is experiencing its first heat wave of 2023, leading to an increase in power demand and spot prices. Peakload is expected to reach a 10-month high, causing spot power prices to climb. SoCal Gas demand is also estimated to reach a two-week high. However, the California Independent System Operator (CAISO) states that the power grid is currently stable with no anticipated supply deficiencies or emergency notifications. Wholesale markets have reacted to the heat wave, with spot prices jumping by 27% and 21% for SP15 and COB, respectively. This is in contrast to record-low power prices observed in May.
Recent draft restrictions in the Panama Canal, due to diminished water levels, have had little impact on LNG shipping flows, according to market sources. While container ships may be affected by the restrictions, LNG carriers with shallower drafts are not significantly impacted. This situation could create favorable conditions for LNG carriers to secure more slots in the canal. The delays have not had a substantial effect on LNG market rates, as LNG freight rates continue to strengthen. The market views the impact as negligible, and day rates for LNG carriers have risen consistently. The delays are not expected to have a significant influence on the market heading into the winter season.
German lignite miners, including LEAG and RWE, are facing concerns that they are exploiting an unfair advantage in Germany’s renewable energy transition. As the country aims to derive 80% of its power from renewables by 2030, the government sees former mining areas as ideal for green development. However, the rapid approvals and significant investments by lignite miners have raised alarms among smaller green developers and local governments in eastern Germany. There are concerns over monopolies, antitrust issues, and the obligations of miners to their legacy. While western Germany sees more muted opposition, there is a focus on increasing local acceptance through cooperative efforts.
The recent surge in mining mergers and acquisitions (M&A) will likely continue until a major miner makes a value-destructive deal, according to Anglo American CEO Duncan Wanblad. He believes that many mining companies are ex-growth and lack the resources and balance sheets needed for exploration and development. Wanblad anticipates one or two destructive deals to occur due to overly optimistic pricing assumptions. Lessons from past mining booms and investor discipline have resulted in more cautious M&A activity in the industry. The demand for copper and other base metals is expected to increase, driving the current round of M&A, but the fundamental problem of supply-demand disparity cannot be solved by M&A alone. Exploration, discovery, and resources development are necessary for long-term solutions.
Chinese seaborne metallurgical coal buying has slowed due to the depreciating yuan and weakening steel margins. The recent decline in steel prices and margins has led to a slowdown in restocking of met coal and coke among steelmakers. Negotiations on the hike in merchant coke prices have stalled, and some merchant cokeries have reduced production, negatively impacting met coal market sentiment. While domestic blast furnace capacity utilization remains high, requests from steelmakers to further cut domestic term coal prices may exert downward pressure on the spot market. Mongolian met coal e-tenders have also cooled, and seaborne PCI trading activity has remained tepid.
Australian prime hard coal prices are expected to have limited upside as more US cargoes enter the Asian market, providing buyers with cheaper alternatives. The influx of US coal and the availability of cheaper coke imports have diverted demand away from Australian met coal supplies. The presence of US cargoes in the market could erode market share for Australian miners. Additionally, the relatively cheap coke imports have led some end-users to replace their met coal requirements with coke. However, Australian prime hard coal supplies for August are anticipated to be more readily available compared to July as one miner increases production and another completes scheduled maintenance.
The Atlantic Basin coal markets remained stable, with limited downward pressure on prompt prices due to supply tightness. Discussions on high-vol A and B coals took place, but no deals were reported. Northwest European thermal coal prices have significantly declined, while natural gas prices in Europe have also retreated. The potential temporary shutdown of ArcelorMittal’s Fos-sur-Mer site and the restart of blast furnaces in Dunkirk and Gijon were notable developments. Salzgitter lifted its force majeure, while Dunaferr suspended rolling operations temporarily. Steel activity in Brazil is slow, and the US market has slowed ahead of the Independence Day holiday. Rosebud Mining’s Mine 78 remains idled, and proposals for SunCoke Energy’s coking coal tender are due. There is potential for a “price warrior” in the tender, but producer restraint is possible due to increased costs.









